The verbal reasoning section of the 11+ exam can be one of the trickiest sections to prepare; it assess your ability to understand, reason and solve problems using framed concepts or written information quickly and accurately. Verbal reasoning tests pupils skills rather than their learned knowledge. The test is used to determine pupils critical thinking skills and their ability to use their own knowledge to solve questions.
The test varies depending on what examination board the school your child is applying for follows. The different board has different styles; some may have more questions than others. For example, GL (Granada Learning) Verbal Reasoning tests are structured differently than the (Centre for Evaluation and Monitoring) CEM exam.
A child’s ability to pass the verbal reasoning test will depend in part on what he or she has learned up until that point. The type of preparation a student undergoes can make all the difference with respect to how well they do in their 11 plus exam, and that is why both parents and children need to know in advance which exam board will administer the 11 plus test. After knowing which board will assess your child’s 11 plus exam you can start your child’s preparation accordingly.
What skills are required in verbal reasoning tests?
As we know, verbal reasoning tests the problem-solving ability of a child and how effectively they can process written information. Verbal reasoning is not based on a child’s learned knowledge, and most children sitting for the 11 plus exam will face this verbal reasoning test for the first time in their life as it is not a part of the National Curriculum in state primary schools. This is the reason why it is essential to familiarise children with the type of questions and style of testing.
The topics of the 11 plus verbal reasoning exam differ based on exam styles and region to region as there is a wide range of questions that can be included, these questions usually require children to-
- Process verbal information
- Apply logical thinking and problem-solving skills
- Find and follow patterns and rules
- Determine word meaning
- Spell accurately
- Apply basic maths skills
- Work systematically
Types of questions in the verbal reasoning section
There are generally two test providers that conduct 11 plus exams. There are a few differences between examination types conducted by both boards. Questions can be either multiple-choice format, matching, true-false cannot say questions or short answers.
The two exam boards are –
GL assessments
The GL exam board covers up to 21 different verbal reasoning skills.
These questions need pupils to find the correct answer from a selection of options using their problem-solving abilities. The 21 topics covered in the 11 plus exam conducted by the GL assessment are-
1. Insert a letter
In these types of questions, pupils need to find out a single letter that must fit into both sets of brackets in order to complete the word in front of the bracket and the word after the bracket.
| Example | sea [?] runk fi [?] ub |
| A. p B. n C. f D. t E. c | |
| Answer | t |
| Explanation | The same letter that fits both sets of brackets to form four words is “t” |
2. Two odd ones outs
These questions are similar to odd ones out where instead of one, the applicant has to choose two words that do not go with the other three. In the below question, five words are given, out of which 3 are related in some way. Students have to find out the two words that do not go with the other three matching words and mark those two words on the answer sheet.
| Example | Black hut green mouse red |
| A. black B. hut C. green D. mouse E. red | |
| Answer | mouse hut |
| Explanation | The words ‘black’, ‘green’ and ‘red’ are related to each other because all three of them are colours, whereas the other two words ‘mouse’ and ‘hut’ do not go with these three words. |
3. Related words
In these types of questions, a code is assigned to each word, and pupils need to deduce the connection between the word and the code. Using the connection between them and applying that to the other word, students need to find the code for the next word.
| Example | If the code for FOOT is ENNS, what is the code for TOE? |
| A. STU B. SND C. UPF D. SRQ E. SNE | |
| Answer | SND |
| Explanation | Using the given information, if the code for FOOT is ENNS, then the code for F is E, O is N, and the code for T is S. Deducing the given information, the code letter is the letter that comes before the letter in alphabetical order. Using the same logic, the code for TOE is SND, where the code for T is S, the code for O is N, and the code for E is D. |
4. Closest meaning
In these questions, five words are there. Two of them, out of which are related in some way. Students need to find the relation between the two words and mark them on the answer sheet.
| Example | Black hut green mouse red |
| A. black B. hut C. green D. mouse E. red | |
| Answer | mouse hut |
| Explanation | The words ‘black’, ‘green’ and ‘red’ are related to each other because all three of them are colours, whereas the other two words ‘mouse’ and ‘hut’ do not go with these three words. |
5. Hidden word
In these sentences, students need to select the option in which there is a pair of words that are next to each other. The selected options should have a word hidden between the two words.
In the below given example, a four-letter word is hidden between the two words and you need to find the pair of words and mark them on the answer sheet.
| Example | The film ended happily after all. |
| A. The film B. film ended C. ended happily D. happily after E. after all | |
| Answer | film ended |
| Explanation | The answer is ‘film ended’ as the hidden word four-letter word is ‘mend’, which is made up of the last letter of the word ‘film’ and the first three letters of the word ‘ended’. a |
6. Missing word
In these types of questions, a particular word in the sentence is incomplete students have to find the part of the missing word from the number of options that can complete the incomplete word in the sentence and mark that on the answer sheet.
| Example | The cat scratched him with his CS |
| A. LAD B. LAW C. HAD D. RAW E. RED | |
| Answer | LAW |
| Explanation | ‘LAW’ is the three-letter word that has been removed from CS. |
7. Letters for numbers
In these types of questions, each letter is assigned to a certain number, and an equation is given using these letters, students need to solve the equation and deduce the sum of the letters using the assigned numbers and mark the answer on the sheet.
| Example | If A = 1, B = 2, C = 3, D = 6, E = 8, what is the answer to this sum written as a letter? A + B + C = [ ? ] |
| A. A B. B C. C D. D E. E | |
| Answer | D |
| Explanation | Converting the letters into numbers, and solving the equation we get 6, and therefore, the answer to this sum is 6. |
8. Move a letter
In these types of questions, there are two words. Students need to move the letter from the first word to the second word in such a way that both the words make sense.
| Example | pound or |
| A. p B. o C. u D. n E. d | |
| Answer | u |
| Explanation | u is the correct option as when you remove u from the word ‘pound’, we get a new word ‘pond’ and when u is added to the word ‘or’ it will result in the new word ‘our’. |
9. Letter series
These types of questions are based on a series of letters. There can be a combination of more than one series based on the series of letters, students need to deduce the relationship between the sets of letters to find the missing preceding pair of letters.
| Example | CQ DQ EP FP [ ? ] |
| A. GP B. GO C. HO D. GR E. GQ | |
| Answer | GO |
| Explanation | The first letter of each pair is in alphabetical order- C, D, E, F and the second letter of each pair appears twice in the series but in reverse alphabetical order- Q, Q, P, P. Following this pattern, the next pair of the letter must be GO. |
10. Word connections
In word connection, there are two groups of words. Each group has a set of one word outside the bracket and a set of words inside the bracket. Students need to deduce the same relationship between the word outside the bracket with one of the words inside the bracket. There is a relation between both words. The students then need to mark both the word in the answer sheet.
| Example | Big is to ( small orange colour) as wide is to (apple red narrow) |
| A. small X. apple B. orange Y. red C. colour Z. narrow | |
| Answer | small narrow |
| Explanation | In the given question, the correct answer as ‘big’ is to small as ‘wide is to ‘narrow’ is because the word relationships here are antonyms. |
11. Number series
Here, there is a series of numbers that follows a particular equation. Students need to find the next number in the series that continues the series in the most sensible way and mark it on the answer sheet.
| Example | 2 4 6 8 [ ? ] |
| A. 16 B. 11 C. 10 D. 9 E. 12 | |
| Answer | 10 |
| Explanation | In this series, you can see the next number is obtained by adding 2 to the previous digit, so by adding 2 to the last given digit, 8, we can obtain the next number in the series, that is 8 + 2 = 10. For other series, you might need to use different types of operations. |
12. Compound words
In these questions, there are two sets of words. Each set has three words, students have to choose one word from each group, that goes together and make one correctly spelt word without changing the order. The first word from the group should come first and then the words from the second group.
| Example | (out by open) (bite like side) |
| A. out X. bite B. by Y. like C. open Z. side | |
| Answer | out side |
| Explanation | The first word is ‘out’ from the first bracketed group and the second word is ‘side’ from the second bracketed group of words. These two words together complete the word ‘outside’. These two words are the only word that together makes the correctly spelt word. |
13. Make a word
In these types of questions, there are two sets of three words. In the first set, the middle word is formed using the other two words, using the relation between the words in the first group, students need to find the missing word in the second group and then mark it on the answer sheet.
| Example | (man [mat] tip) (bug [ ? } dew) |
| A. bud B. beg C. dug D. bed E. wed | |
| Answer | bud |
| Explanation | From the first set, we can deduce the relationship between the first three words and find the middle word of the second combination. In the first combination, the first two letters of the ‘man’ are put together with the first letter of the third word ‘tip’ to form the middle word ‘mat’. Similarly, using the first two letters of the word ‘bug’ and the first letter of the word ‘dew’, we form the middle term ‘bud’. |
14. Letter connections
In these questions, there are two pairs of two letters. Pupils need to deduce the connection between these pairs and use that connection to find the right option out of the four that goes with the third pair following the same connection that was between the first two pairs.
| Example | AB is to CD as PQ is to [ ? ] |
| A. RT B. SR C. ST D. RS E. QR | |
| Answer | RS |
| Explanation | Deducing the relation of the first two pairs, we get that the letters ‘CD’ come straight after the letters ‘AB’ in the alphabet. The second two pairs of letters should also follow the same relation. ‘RS’ are the letters that come straight after ‘PQ’ in the alphabet series. |
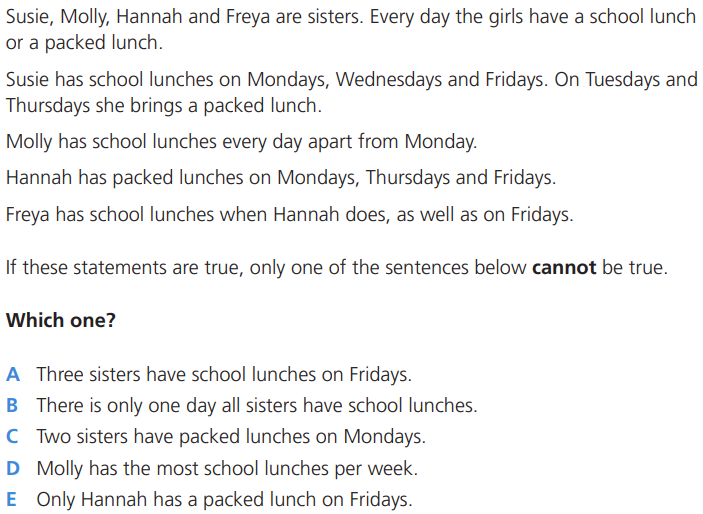
15. Reading information
In “reading information” questions a passage of text is given and related to that few statements are given, based on the passage, you have to deduce which of the given statement is true false or cannot say. Verbal reasoning tests the same skills as aptitude tests and psychometric tests.
16. Opposite meaning
In these types of questions, there are two groups of words, pupils have to choose one word from each group that are exactly opposite in meaning to each other and mark both words on the answer sheet.
| Example | (morning early wake) (late shop dark) |
| A. morning X late B. early Y shop C. wake Z dark | |
| Answer | early late |
| Explanation | The two words from each group that are opposite to each other are ‘early’ from group 1 and ‘late’ from group two. |
17. Complete the sum
In “complete the sum” questions, there is a set of digits given, the applicants need to find out the sum of these digits. Pupils have to choose the correct answer out of the options given and mark it on the answer sheet.
| Example | If A = 1, B = 2, C = 3, D = 6, E = 8, what is the answer to this sum written as a letter? A + B + C = [ ? ] |
| A. A B. B C. C D. D E. E | |
| Answer | D |
| Explanation | While using the given information, if we convert letters into numbers, the answer to the sum will be 6. We can see that 6 is represented by the letter D and hence the answer is D. |
18. Related numbers
In “related numbers” questions, there are two sets of numbers, the sum of both sets of numbers should be equal to each other. Pupils have to find the missing number that will complete the equation correctly and mark it on the answer sheet.
| Example | 3 + 5 = 6 + [ ? ] |
| A. 1 B. 2 C. 3 D. 4 E. 5 | |
| Answer | 2 |
| Explanation | In the example, sum of the right must be equal to the sum on the left. Pupils have to find the number from the options that can replace the question mark, making the sum of both sides equal. The sum on the left gives 8, so the question mark must be 2, as 6 added with 2 also makes 8. |
19. Word number codes
In these types of questions, pupils are given four words, three of them, out of which have a code. The codes are not in the same order as the words. Pupils need to work out the correct answer for the word and mark them on the answer sheet.
Prepare for 11+ Success
Get instant access to 5000+ practice questions and expert guidance
| Example | Three of these four words are given in code. The codes are not written in the same order as the words and one code is missing. |
| ANTS BASE LETS BLUE 5836 4172 8672 | |
| Explanation | To answer this type of question, pupils need to deduce which number represent which code. Let’s start with focussing on one number which appears more than one. If this number appears in the same position in two of the codes, it might help you in spotting the same pattern with the letters. If you are not able to do that, you can compare the position of your chosen letter and check if the same is reflected in the words given. In the given example, 8 number appears in two number codes 8672 and 5836. This means it could be letter A or L. Factoring the position of 6 as well, the number 8 has to stand for the letter L. 6 stands for E, Knowing BLUE = 5836 AND LETS = 8672, we can obtain what other letters stand for and find the answer for missing words or codes. |
20. Complete the word
In these questions, there are two groups of words where the words in the second group should relate to each other in the same way as the three words in the first group. Here, pupils have to find the missing word of the second group by deducing the relation between the words in the first group. Pupils then need to mark the answers on the answer sheet.
| Example | (man [mat] tip) (bug [ ? } dew) |
| A. bud B. beg C. dug D. bed E. wed | |
| Answer | bud |
| Explanation | From the first set, we can deduce the relationship between the first three words and find the middle word of the second combination. In the first combination, the first two letters of the ‘man’ are put together with the first letter of the third word ‘tip’ to form the middle word ‘mat’. Similarly, using the first two letters of the word ‘bug’ and the first letter of the word ‘dew’, we form the middle term ‘bud’. |
21. Same meaning
In these types of questions, there are five options given. Pupils have to select out the word, out of the five words, that are best connected to the words in both brackets.
To solve these types of questions, the trick is to find the word that would fit equally into both sets of brackets or to look for an option with at least two different meanings
| Example | (world globe) (soil ground) |
| A. ball B. dirt C. plant D. earth E. universe | |
| Answer | earth |
| Explanation | The correct answer is ‘earth’ as the words go equally well with both pairs of words. It refers to the planet Earth (world, globe) and also refers to the ground (soil, ground). |
CEM exams
The CEM board does not tend to clearly define the topics covered in the 11 plus exam. Verbal reasoning is commonly assessed as a part of the 11 plus English test. Based on the past English papers, the few topics covered in the verbal reasoning section are –
1. Jumbled sentences
2. Cloze passages
3. Cloze sentences
4. Synonyms/Antonyms
How to prepare for the Verbal Reasoning Test?
The Verbal Reasoning Test is a part of the 11 plus exam. It is designed to measure a child’s critical reasoning skills and its ability to read, understand, and use language. The questions in verbal reasoning test a child’s vocabulary, grammar, comprehension and spelling skills.
The verbal reasoning section also sometimes include reading comprehension and passage completion. Reading comprehension includes questions that test your understanding of what you read, while passage completions refer to questions that ask about words or phrases in a sentence or sentence completion questions. These are questions based on the passage of text where you have to choose the correct word from several possibilities.
Regular reading and word games
It is important to practice reading for at least 30 minutes per day if you want to improve your child’s vocabulary skills. Your child should also practice grammatical skills by focusing on verbs, nouns and prepositions. You can do this by solving crossword puzzles or playing word games on the internet.
Practice papers
Some questions might be about the meaning of a word in the passage or about something that is not explicitly stated in the passage but can be inferred from information in the passage. Whereas, some questions can be harder to understand for children as they will be facing them for the first time for such questions, the best way to prepare is through practice tests. The practice verbal reasoning test will help develop an understanding of different question types and workout strategies for answering them.
Past papers
The other way to get your child to familiarise with the type of question is past papers. Past papers help kids to familiarise themselves with different types of questions, and further help them gain an understanding of time management and how they can finish the entire paper under timed conditions. It is also a good way to test the verbal reasoning ability of your child.
Take help from books and courses
If you want to prepare for this test, you should find a good verbal reasoning practice book or course for this purpose. You can also take preparation courses from experts in this field.
Why is the verbal reasoning practice test important?
The verbal reasoning part of the test is important because it tests a student’s ability to think flexibly and quickly.
Verbal reasoning is a mental ability that allows you to solve problems and answer questions involving verbal material, such as words, sentences, or paragraphs.
The verbal reasoning practice test is important because it helps the student to improve their language and reasoning skills, especially for those who are not well-versed in English.
Tips to follow when preparing for VR
Practise different solving strategies.
The different question requires different solving strategies, you can help your child to work on different strategies so they can know which strategies work best for them. For instance, when it comes to comprehension, some people like to read the passage first and then look at the statement whereas others like to read the statement first and then look at the passage.
Manage your time carefully
In most 11 plus exams, which includes questions that test verbal reasoning skills, each question should be answered within 1 minute or less. To complete the entire paper in time, kids need to manage their time carefully including the time taken for the other assessment centre activities.
Fact-based decision-making process
When it comes to passage and comprehension, pupils must not use facts or real-life intelligence that they know. Pupils should only use the facts mentioned in the passage if anything is not included in your passages, it shouldn’t be included in your answering process.
Practice regularly
Regular practice always helps in improving the ability to perform well, especially when it comes to exams like verbal ability tests where these tests are used to assess students ability to understand and solve problems using the given information and not the learned knowledge. Regular practice not only improves ones ability to perform well but also improves a child’s confidence and help them to relax.
Stay calm and focused
When it comes to verbal reasoning, tests are timed, and some people find it hard to focus and complete the test under timed conditions and to answer all the questions quickly and accurately, a person needs to stay calm and focused.
Try starting at the end of the sentence when stuck
As we know, there are several text passages and complicated questions which can be difficult to understand, in such a situation a great way to unravel a complicated question is to start at the end of the sentence and read backwords. This can be very useful in decoding the meaning of contradictory points and circular references.
Read the questions carefully
The most important tip to follow when attempting the VR paper is to read the questions carefully. One should keep in mind that these questions are deliberately formed in a complicated way so to deduce the answers, one must read the questions or passages carefully.
Free verbal reasoning test
You can try Free Familiarisation Materials provided by GL assessment. You can test the verbal reasoning skills of your child by asking them to solve these papers. The GL paper tests verbal reasoning abilities, verbal tests generally check the student’s ability to comprehend the written question. The other papers include the non-verbal reasoning test, verbal reasoning test, English and mathematics.
